
AUGMENTED REALITY MAINTENANCE
Augmented reality offers the opportunity to make maintenance and servicing processes in industry much more efficient. Our smart glasses guide explains how augmented reality can be used in industry and presents tried-and-tested models.
WHAT IS AUGMENTED REALITY?
Augmented reality, or AR for short, is a process in which virtual elements are added to reality or an actual "material scene". Augmented reality is not the same as virtual reality, as there is no immersion in a completely virtual world. With AR, the actual sense stimulation remains present - a crucial aspect in the context of maintenance and service.

BOTH HANDS FREE FOR WORK TO BE DONE
Augmented reality can be implemented with a wide variety of hardware, anddata glasses, also known as smart glasses, are particularly recommended for maintenance processes in industrial companies.
Data glasses display context-relevant information in the user's field of vision. It is therefore no longer necessary to look at a smartphone or tablet and hands remain free.
In general, a distinction can be made between two technologies: AR light and 100% AR. Our data glasses guide will help you find the right data glasses for your individual service and maintenance requirements.

AR SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR COMPANY
We have been realising augmented reality solutions for industry for over 10 years. With bitnamic CONNECT, we offer you a powerful platform that combines numerous tried-and-tested AR functions for direct use in your company. At the same time, our system forms the modern basis for your customised AR projects - whether WebXR, Unity, ARCore or ARKit. Bitnamic is your reliable development partner for innovative AR solutions.

GETTING STARTED WITH AR/VR
Webinar recording
Learn from our CEO and co-founder Rolf Behrens what Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR) and Extended Reality (XR) are.
After watching you will know which hardware and software offers which possibilities. And all this is accompanied by practical and understandable examples from industry and SMEs.
(Recording in german language - soon with EN subtitles)
Length: 30 min.

SMART GLASSES AS THE IDEAL ENTRY INTO AUGMENTED REALITY MAINTENANCE
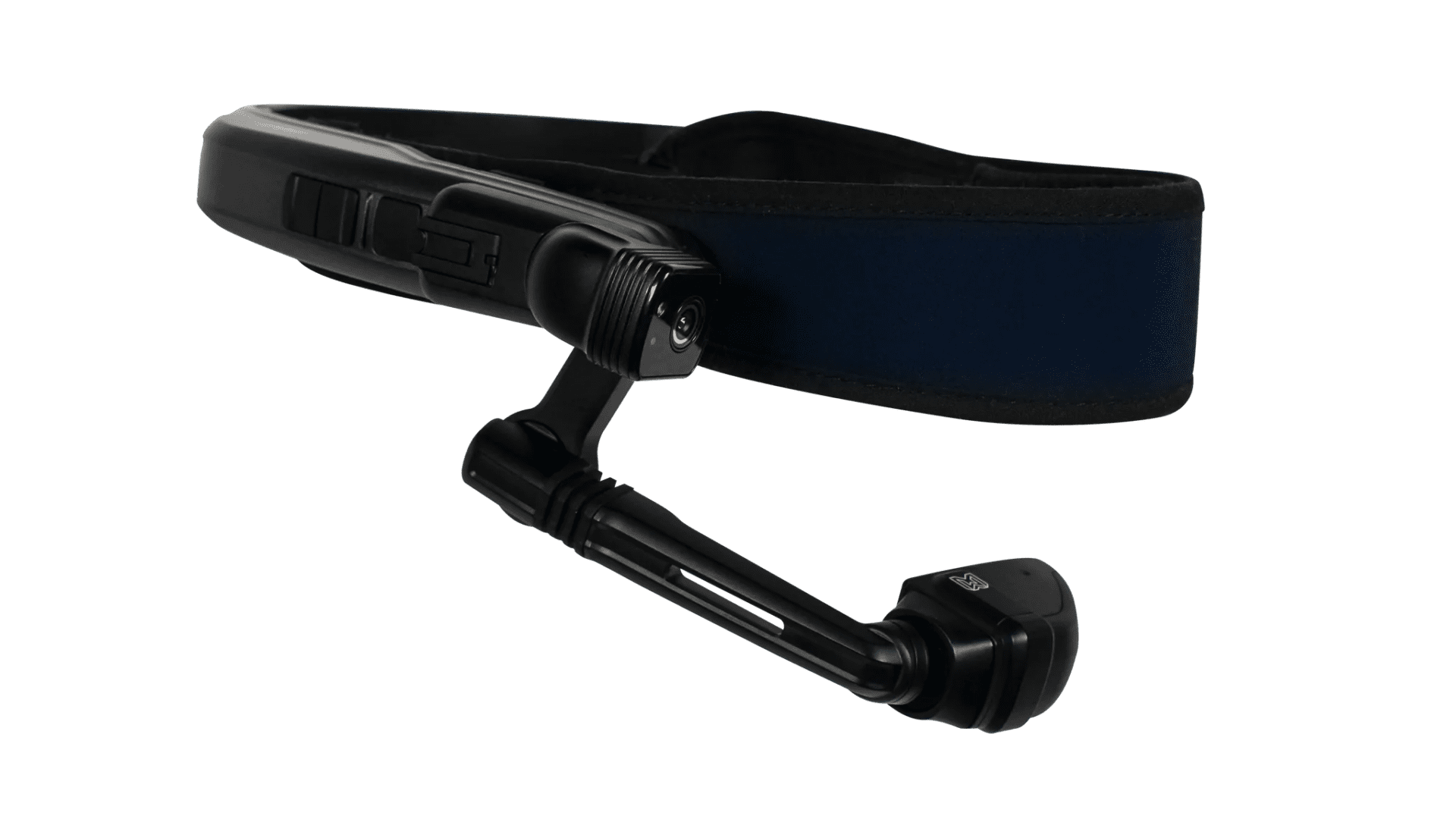
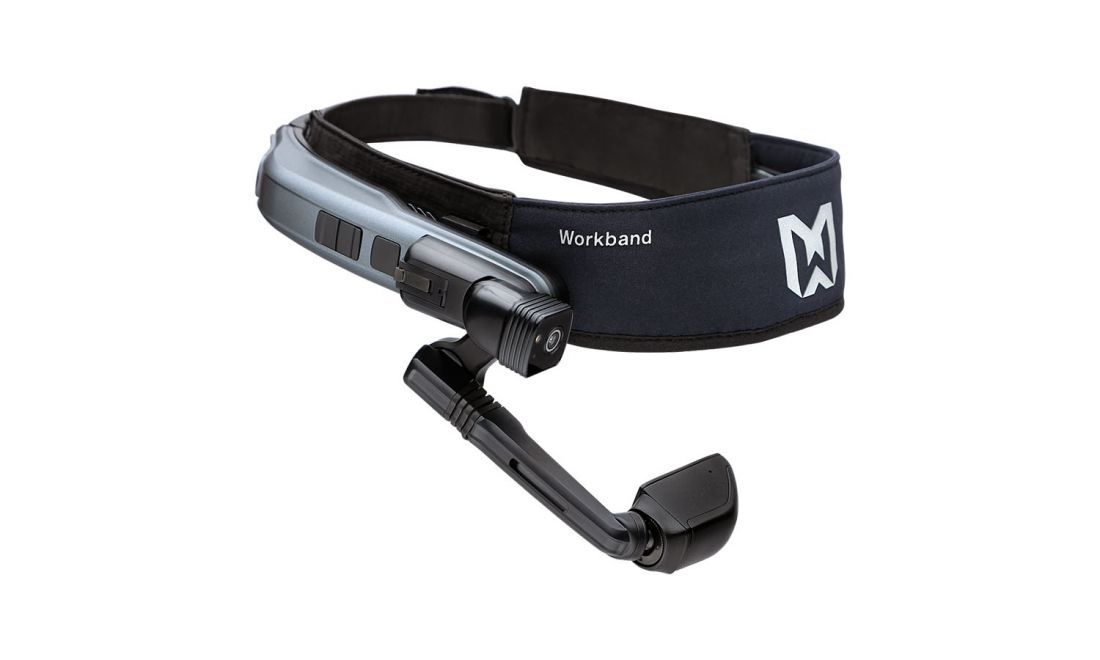
Android-based data glasses such as the RealWear Navigator 520 or VUZIX M400 models are located between standard platforms and AR. This can be referred to as AR light, as there is no direct reality overlay. The data glasses have a 2D assistance screen located in the peripheral field of vision. Information can be sent to the external expertvia this screen - for example with the help of the bitnamic CONNECT Service HUB. At the same time , videos, application windows, documents, etc. can be received from the expert via screen sharing. The integrated microphone also enables verbal communication.
Data glasses promote efficient troubleshooting: as the camera is in the immediate vicinity of the eye, the expert can more quickly understand which component the service technician is focusing on and give appropriate instructions. Triggered functions such as annotations or laser pointers, which characterize our visual support software, are transferred directly to the screen of the data glasses.

THE FULL AUGMENTED REALITY EXPERIENCE
The Microsoft HoloLens enables advanced augmented reality maintenance. The head-mounted display (HMD) offers extensive possibilities and functions, such as spatial detection using sensors, spatially appropriate visualization or the exact superimposition of real objects.
Integrate any number of 3D objects and benefit from significantly more placement options thanks to the display of virtual elements in the entire real space - in contrast to the limitations of classic 2D displays. Thanks to positioning in the entire field of view, including spatial anchoring, the virtual objects always remain in their original physical location, even if you as the wearer change your position.
With the Microsoft HoloLens, you can merge reality with virtual content and facilitate all workflows in maintenance processes thanks to the resulting spatially appropriate overlays.

THE FOLLOWING REFERENCE MODELS ARE OFFICIALLY SUPPORTED BY BITANMIC:
Find out more about the new Navigator series from RealWear in our comparison between Navigator 520 and Navigator 500.
You can find a direct comparison of RealWear Navigator 520, Vuzix M400 and Microsoft HoloLens 2 in our article Smart Glasses for industry | The top 3 in comparison.

- Android 11 platform
- 1,280 x 720 pixel HyperDisplay
- 48 MP camera
- Pure voice control (can also be used offline, available in 17 languages)
- IP66 MIL-STD 810 H certified
- 6-8 hours battery life, hot-swappable
- Additional micro SD card slot for sufficient storage space
- Compatible with security equipment
- Noise suppression up to 100 dBA

- Android 11 platform
- 854 x 480 pixel MicroDisplay
- 48 MP camera
- Pure voice control (can also be used offline, available in 17 languages)
- IP66 MIL-STD 810 G certified
- 6-8 hours battery life, hot-swappable
- Additional micro SD card slot for sufficient storage space
- Compatible with security equipment
- Noise suppression up to 100 dBA

- Android 9 platform
- OLED screen > 10,000:1 contrast ratio
- 12.8 MP camera, 4K video
- Phase Detect Autofocus (PDAF), optical stabilization
- Voice control (customizable, supports multiple languages)
- 3 control buttons and a 2-axis touchpad with multi-finger support
- IP67-certified
- Drop resistance up to 2 meters
- Hot-swappable 2-12 hours battery life (depending on choice of external battery)

- Windows Holographic operating system
- Transparent holographic lenses (waveguides)
- 2k 3:2 light generator resolution
- 4 visible light cameras, 2 IR cameras
- 8 MP camera, 1080p30 video
- Real-time tracking (eye-tracking)
- Voice control (commands and control on the device, natural language with internet connection)
- Real-time environmental integration
- Photos and videos mixed from hologram and physical environment
- 2-3 hours battery life (active use)

- visionOS
- 2x micro OLED display with 23 million pixels each
- 12 cameras, 5 sensors
- eye tracking
- Spatial audio (HRTF)
- Control with eyes, hands and voice
- Dual-chip processor
- 2 hours battery life
- On request, we can check direct compatibility
- or a possible porting to data glasses from your inventory.
ULTRASONIC MEASUREMENT WITH AR IN AVIATION
Challenge
A component from aircraft construction is to be inspected for material defects. An ultrasonic measuring device is used for so-called non-destructive material testing: This method makes it possible to carry out material testing without causing damage to the component
The technician usually has to look at the screen of the device to which the measuring device is connected (e.g. a laptop). This is no longer necessary with the use of the Microsoft HoloLens, making work more efficient.
How augmented reality supports
With the help of bitnamic CONNECT, a Hololens application guides the user step by step through the entire testing process. Overlaid texts and images show the user which action is required in the current step or how this action is to be carried out. In the course of the scenario, possible fault areas are indicated by animated markings, which the user should then check with the ultrasonic measuring device. After a measurement process, the result is displayed directly above the inspected area on the component. This makes the inspection significantly faster and minimizes errors. The device can be operated completely hands-free. This scenario has already been subjected to a large number of user tests and has shown consistently positive results.IOT-INTEGRATION
The scenario described below shows a possible integration of machine data in combination with the advantages of our remote maintenance solution.
An industrial robot is visualized three-dimensionally in space (provided by Salt and Pepper). The industrial robot is part of a production plant and is equipped with various sensors. The sensor values are transmitted to our servers by the Beat Monitoring System (BMS) and visualized live on display elements on the model.
The data is synchronized with our servers. If an error occurs on the industrial robot, the HoloLens user is informed. The affected component of the robot is highlighted in color and the corresponding error text appears.







