Image: See collaboration as an opportunity. Identify and utilise further developments in robotics, AI and AI as support.
How modern engineering companies deal with current challenges, which innovative solutions really support a sustainable future and what role visual support plays in this.
Reading time: approx. 8 minutes
Of interest to: Service management, maintenance, after sales, plant and machine manufacturers, field services, industrial manufacturing companies (with facts & figures from German companies and statistics)
Content:
- Challenges in machine construction
- The role of digital transformation in the future of machine engineering
- Innovative service solutions as the key to success
- How should a machine manufacturer be digitally positioned in 2025??
- Bitnamic: The missing puzzle piece in mechanical engineering
- Outlook and future visions for mechanical engineering
I. Challenges in machine construction
Manufacturing and industrial companies are facing various challenges. According to a DIHK survey (chart in german language), the three biggest business risks include increased energy prices, the economic policy framework and the shortage of skilled labour. These and other factors have a huge impact on the industry and require innovative solutions in order to remain competitive and meet future requirements.
ENERGY AND RAW MATERIAL PRICES
According to the DIHK survey, rising prices in the energy and raw materials sector are the biggest challenge for mechanical engineering. Companies are called upon to develop more energy-efficient solutions and optimise their production processes in order to reduce costs and operate more sustainably.
ECONOMIC POLICY CONDITIONS
Pandemic, wars and a faltering economic policy. Not an easy basis for making far-reaching decisions.
SHORTAGE OF SKILLED WORKERS
The shortage of specialised staff is not disappearing and is proving to be a major problem for the mechanical engineering industry.
- On the one hand, employees who ‘know machines like the back of their hand’ are retiring.
- On the other hand, well-trained young talent is in short supply.
It is becoming increasingly difficult to find qualified employees with the necessary expertise. To meet this challenge effectively, companies are taking strategic measures to challenge, promote and retain their employees.
COMPLEXITY
Products in the engineering sector are becoming increasingly complex and there is a growing variety of models, which poses challenges for development, production and maintenance. Companies must therefore optimise their processes and find innovative solutions to master this complexity and increase efficiency.
PRICE PRINT
Price pressure within the industry is high. Customers demand cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Companies must therefore optimise their cost structures and offer innovative products and services at the same time in order to remain competitive.
DIGITISATION | Industry 4.0 | IoT (Internet of Things) & AI
Digital transformation plays a decisive role in the future of mechanical engineering. Companies that rely on the ‘tried and tested’ and still say things like ‘That’s always worked’, which do not digitalise their business models and processes, will not be competitive in the long term and will miss the opportunity to take advantage of new digital opportunities. The development of a digital strategy is therefore of great importance in order to exploit the potential of digitalisation and ensure the future viability of the company.
If that wasn’t enough of a challenge, there are other issues on top such as spare parts management, a properly functioning service hotline, the documentation of machines and systems (e.g. user manuals), quality management, warranty management and finding a suitable successor for the company at some point (especially in the small and medium-sized enterprise sector).
In its report Company Succession 2024 (only available in german language) the DIHK estimates that the existence of more than 250,000 companies could be jeopardised in the next five years — not only because the search for suitable interested parties fails, but also due to increasing bureaucracy, uncertainty and costs.
– But how do you deal with all these challenges and still remain competitive? –
II. The role of digital transformation in the future of machine engineering
The digital transformation will have a significant impact on mechanical engineering in the coming years. By using digital technologies and data, companies can optimise their processes, increase efficiency and open up new business opportunities.
The digital transformation enables connected production and improved communication along the entire value chain. By using Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, big data and artificial intelligence, companies can monitor, analyse and optimise their production processes. This enables them to reduce costs, improve quality and respond more flexibly to customer requirements. And who doesn’t want to offer a perfect customer- or service experience?
In addition, the digital transformation is opening up new business models and services. However, this also requires a change in corporate culture and working methods. Companies need to embrace this, recognise opportunities, prepare their workforce for the new requirements and involve them in the digital transformation. Open communication, further training and the promotion of digital skills are crucial to ensure the success of the digital transformation.
III. Innovative service solutions as the key to success
Excellent service solutions are crucial to the success of mechanical engineering companies. They enable problems to be identified quickly, maintenance work to be carried out efficiently and downtimes to be minimised.
On the one hand, there is software that is able to record and analyse data from machines in order to identify potential problems at an early stage. By using predictive maintenance*, maintenance work can be planned and downtimes minimised.
On the other hand, visual support software gives you the opportunity to offer your customers improved 24/7 support. The software has many convincing advantages: it relieves employees by saving manpower so that they only have to travel to the ‘really big service cases’. This saves resources (shortage of specialised staff), minimises costs for travel, maintenance & servicing and machine downtime. Companies that rely on such software improve their service experience for their customers and their own team, their ‘time-to-service’ (support in seconds) and, last but not least, their competitiveness.
Visual Support software can be connected to an existing ticket system (e.g. Salesforce, ServiceNow, Dynamics). This enables various billing options and the tracking of processes in tickets. This opens up new sources of revenue and increases customer satisfaction and trust in high-quality service.
All service solutions to be procured should enable you to communicate and collaborate easily, both internally and with customers.
In the coming years, service solutions will become increasingly important in order to remain competitive and meet increasing demands. Companies should therefore invest in innovative service solutions at an early stage and prepare for the future.
* Predictive maintenance is an Industry 4.0 application that is based on the analysis of machine data and proactively maintains systems.
IV. How should a machine manufacturer be digitally positioned in 2025??
According to the MIT Technology Review Insights survey, there are likely to be three main areas of business in 2025 where AI use will become significantly more important compared to 2022. These are
1. IT and
2. finance departments as well as
3. functions related to supply chain and manufacturing processes.
Integration of Industry 4.0 and IoT
Connected machines: Equipping machines with IoT sensors that collect real-time data and send it to centralised platforms.
Data analysis: using big data and AI to analyse the collected data to enable predictive maintenance and optimise machine performance
Automation: Introduction of automated processes such as material flow control by mobile robots & forklifts, systems to increase efficiency and reduce errors.
Assistance from KI/AR
Chat bot: Use of chat bots on websites and conceivably also in applications for internal areas such as sales and after-sales. Knowledge management 24/7 with the support of the intelligent chat bot
Expansion of business
Offering or utilising rental models: Instead of buying machines for millions, a pay-per-use model can be offered, which is billed according to the number of packages or labels, for example. If high machine availability and increased service volumes and services can be guaranteed.
Platform for spare parts business and service
Shop system: Optimisation for a highly transparent purchasing and service platform in the spare parts business. Keep an eye on your spare parts and services portfolio, roll it out to a wide range of platforms and offer a unique user experience thanks to standardised data.
Cyber security
Security systems: Implementing strong security protocols to protect data and systems from cyberattacks. According to Statista, expenditure on IT security in Germany in the years 2017 to 2021 and forecast to 2025 will increase by 1.8 billion to 10.3 billion from 2023 to 2025.
Training: Regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices.
Certifications: Compliance with international security standards and regular audits.
Cloud technologies
Cloud computing: Use of cloud platforms for data management, analysis and remote access to machine data.
Platform independence: Ensuring that all digital systems and tools are available and accessible in the cloud.
Digital twins
Simulation and modelling: Use of digital twins to simulate machines and production processes in order to predict maintenance requirements and optimise production processes.
Real-time monitoring: Use of digital twins for real-time monitoring and fault diagnosis.
Customer interfaces and digital services
Online platforms: Providing online portals and mobile apps through which customers can monitor machines, submit service requests and receive support.
Self-help tools: Development of digital tools such as interactive manuals, tutorials and chatbots to assist customers with troubleshooting.
Customer data analysis: Utilisation of customer feedback and data to continuously improve products and services.
Skilled employees and further training
Training programmes: Continuous training of employees in the latest digital technologies and best practices. Challenge and support.
Hiring: Attracting and retaining talents with digital expertise, among others.
Digital culture: Promoting a corporate culture that supports digital innovation and continuous learning.skultur, die digitale Innovation und kontinuierliches Lernen unterstützt.
Sustainability and resource efficiency
Energy-efficient technologies: Integration of technologies to monitor and reduce the energy consumption of machines.
Sustainable production: use of digital tools to optimise production processes and minimise waste.
Circular value creation: use of digital solutions to support the recycling and reuse of materials.
Partnerships and ecosystems
Co-operations: Establishing partnerships with technology providers, universities and other industry players to promote innovation.
Open innovation: Participation in innovation networks and exchange of best practices and technologies with other companies.
‘A basic assumption … is that future machine offerings will continue to follow the trend towards increasingly complex machine + service + software packages. For machine manufacturers, this means working increasingly in one or more ecosystems, where specialised partners are responsible for data evaluation, software or online services, for example. Within an ecosystem, the leading partner is usually the one that contributes the decisive value-added steps,…’ says Deloitte in the Mechanical Engineering 2030 study.
V Bitnamic: The missing puzzle piece in mechanical engineering
Bitnamic GmbH specialises in digital (AR) software solutions for location-independent service and employee qualification. With bitnamic CONNECT, the company offers three versatile hubs
– Visual Support, Documentation & Academy –
in one product to speed up service processes, save costs and effectively counteract the shortage of specialised staff. Companies from various industries (including aerospace, automotive and pharmaceuticals) benefit from service optimisation, employee enablement and digital transformation.

bitnamic CONNECT — Visual Support
In the event of a service issue, support technicians on site at systems and machines by solving problems remotely together with experts using live video and augmented reality.
Watch the Visual Support (Remote Maintenance) video here
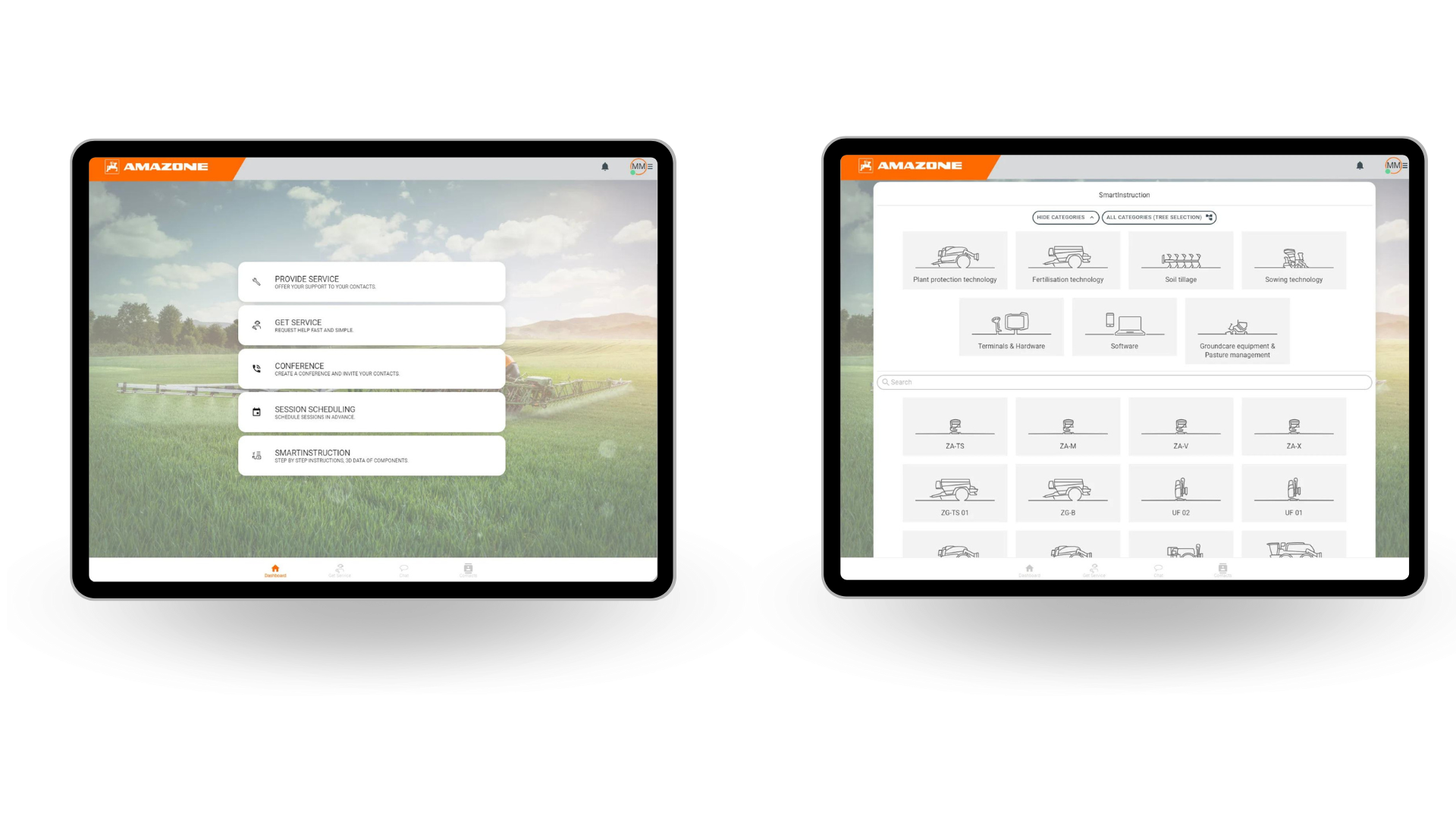
bitnamic CONNECT — Documentation Hub
Quick access to documentation and instructions. Provide digital knowledge such as manuals, documentation, instructions, etc. for quick and easy access, anytime, anywhere.
Watch the Documentation Hub video here

bitnamic CONNECT — Academy
Provide customer and employee training as well as onboarding, with targeted knowledge queries for empowerment digitally in order to build up expertise in a sustainable and qualified manner.
Click here to watch the Academy video.
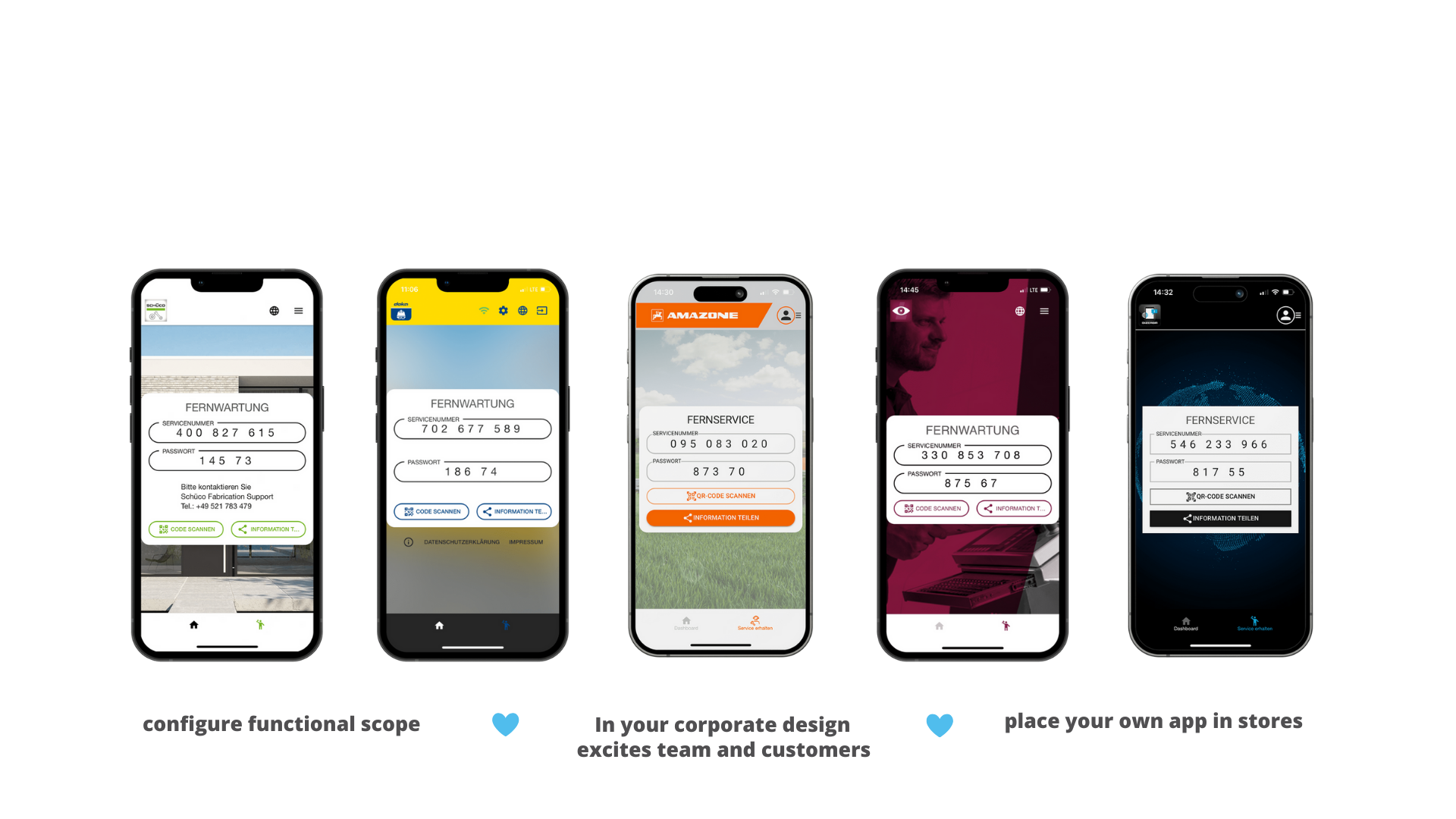
Whitelabeling. Own branding — your customised service app. (Brand Kit)
One visual support software — different look & feels. Your software in your corporate design.
Integration into existing ticket systems
In service, different solutions are often used for troubleshooting and providing service. In most cases, so-called ticket systems are used, which are used for receiving requests and communicating to resolve problems.
Our solution connects Visual Support directly to your ticket system and/or customer portal, e.g. ServiceNow, MS Dynamics or Salesforce.
Generally, these systems are the central point of contact for service department and are deeply embedded in the company’s processes. They also store important data that can be used to improve the company’s own products and service.
It is therefore all the more important that data islands and non-integrated software solutions are avoided, i.e. that functions such as visual support (remote maintenance) can be accessed from the ticket system.
That’s exactly what we provide with bitnamic CONNECT.

Do you have any questions about integrations or would you like to find out more about bitnamic CONNECT? Contact us today!
VI Outlook and future visions for mechanical engineering
Engineering is facing an exciting future full of opportunities and challenges. If companies embrace the digital transformation, they will be able to develop innovative solutions to remain competitive.
Future visions for engineering include the advanced use of rental models, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, the automation of processes and the integration of IoT technologies into production, all the way to the smart factory.
In addition, service solutions such as those developed by Bitnamic will play an increasingly important role. By using visual support software, companies are able to improve their service quality, minimise downtimes and enhance the customer experience.
Therefore, it is important that companies recognise the opportunities of digitalisation at an early stage and invest in innovative solutions. This is the only effective way to successfully meet the challenges of the future and shape a sustainable path forward in mechanical engineering.
*
On the topic:

Whitepaper
Checklist for the implementation of visual support / remote maintenance software
(Currently only available in German. Please contact us if you are interested!)
Sources (mostly available in German language):
1. https://www.dihk.de/de/aktuelles-und-presse/aktuelle-informationen/deutschlands-mittelstand-tragende-wirtschaftssaeule-geraet-unter-stress-120978 Accessed on August 16, 2024
2. Statistik: DIHK. (15. Februar, 2024). Welche Geschäftsrisiken sehen Sie für Ihre Unternehmen innerhalb der nächsten Monate? [Graph]. In Statista. Accessed on June 11, 2024, from https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/1290347/umfrage/geschaeftsrisiken-fuer-die-deutsche-industrie/
3. https://de.statista.com/infografik/30520/geschaeftsbereiche-in-denen-ki-als-zentraler-bestandteil-gilt-gelten-wird/
4. Statistik. (Statista 2024) Ausgaben für IT-Sicherheit in Deutschland in den Jahren 2017 bis 2021 und Prognose bis 2025, Accessed on August 19, 2024 by, https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/1041736/umfrage/ausgaben-fuer-it-security-in-deutschland/
5. Deloitte. Maschinenbau 2030. Vier Szenarien für den Wachstumsmotor Maschinenbau. Accessed on August 19, 2024 https://www2.deloitte.com/de/de/pages/energy-and-resources/articles/maschinenbau-2030.html




